For many NRIs, India is like light from a distant galaxy.. they see the version of it that existed when they left, not the one that’s evolved since…
— Nishchay (@agNishchay) May 27, 2025
Back in my day… yes sir, that day was two governments and one Jio launch ago…
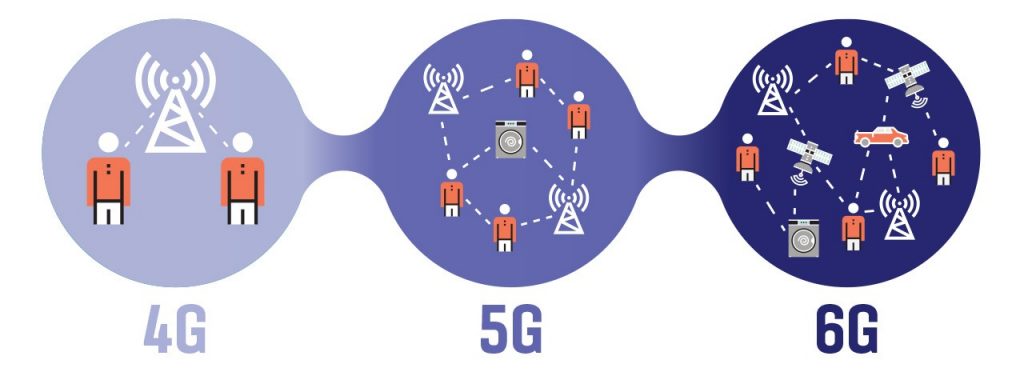
5G Penetration in India
- Research Partnerships: Jio Platforms has partnered with Finland’s University of Oulu for 6G research and standardization. Ericsson collaborates with IIT Madras’s Centre for Responsible AI (CeRAI) to align with India’s 6G goals.
- Indigenous Standards: The success of the 5Gi standard, merged with global 5G standards by 3GPP, demonstrates India’s growing influence in global telecom standards.
- Talent and Ecosystem Development: India is investing in state-of-the-art research facilities, incentives for startups, and talent development to build a robust 6G ecosystem. However, funding remains a challenge, with India’s FY25 telecom R&D budget at ₹1,100 crore (0.03% of GDP), significantly lower than China’s $1.55 trillion allocation. Experts suggest tapping into the ₹83,468 crore Universal Services Obligation Fund (USOF) to boost 6G research.
- United States:
- Feasibility: India’s ambition to secure 10% of 6G patents and its collaboration with the US through initiatives like iCET (Initiative on Critical and Emerging Technologies) signal potential for technology partnerships. However, the US is investing heavily in 6G (e.g., $2.5 billion with Japan) and has its own Next G Alliance, making it a competitive market. India’s lack of significant 6G patent filings as of 2021 and reliance on foreign equipment could limit its export potential.
- Timeline: Exporting 6G to the US by 2030 is unlikely due to the US’s advanced domestic efforts and security concerns over foreign tech (e.g., bans on Huawei). India might contribute niche solutions or software by 2035, provided it ramps up IP development and aligns with US standards.
- Europe:
- Feasibility: Europe lags in 5G deployment compared to India and China, with only 45% mid-band coverage by 2024. India’s cost-effective manufacturing and software expertise could position it to supply 6G solutions, especially if it aligns with European standards via 3GPP. However, Europe’s preference for Nokia and Ericsson and concerns over non-European suppliers may pose barriers.
- Timeline: India could potentially export 6G components or software to Europe by 2032–2035, leveraging its growing influence in global standards and partnerships with European institutions like the University of Oulu.
- Africa:
- Feasibility: Africa has low 5G penetration (10–15% mid-band coverage by 2024), making it a promising market for affordable 6G solutions. India’s experience with 5Gi for rural coverage and its focus on cost-sensitive markets align well with Africa’s needs. India’s telecom giants like Jio and Airtel could partner with African operators to deploy 6G, especially with ITU’s support for affordable connectivity.
- Timeline: India is well-positioned to export 6G technology to Africa by 2030–2032, potentially earlier than to the US or Europe, due to less competition and alignment with Africa’s connectivity goals.
- Funding: The modest R&D budget compared to China and the US limits India’s ability to compete in patent filings and infrastructure upgrades.
- Infrastructure: Upgrading existing 4G/5G networks for 6G requires substantial investment, with high operational costs for energy and maintenance.
- Global Competition: China’s lead in 6G patents and early satellite tests (e.g., the 2020 6G satellite launch) and the US’s strategic alliances pose challenges.
- Africa: 2030–2032
- Europe: 2032–2035
- US: 2035 or later
The Democratic party industrialized America under FDR, led us to win WWII, established the minimum wage, social security, Medicare, Medicaid, affordable care, signed civil rights & voting rights and is pushing for universal childcare & healthcare.
— Ro Khanna (@RoKhanna) May 27, 2025
We are not "weak and woke."








.jpg)